This article is specially designed to give you the basic knowledge of computer, so it will clear the basics of computer.
What is a computer? #Who invented the computer? #What can computers do? #classification of computer -You can see the related topics from all these.
#What is a computer?
In this we will tell you computer basic which I hope will be important for you Come see A computer is an electronic device for storing and processing data, usually in binary form, by converting it into a variable program with instructions given in it. Have to act accordingly. A computer is an electronic device that manipulates information or data. It has the ability to store, and process data, data processing, manipulation of data by computer, retrieve Data retrieval means retrieving data from database {Management System (DBMS) like ODBMS}.
Machine-readable form, the flow of data through CPU and memory to output devices and transformation. Any use of a computer to perform defined operations on data can be included under data processing. In the business world, data processing refers to the processing of data required to run organizations and businesses You already know that you can use a computer to write documents, send emails, play games, and browse the web. Even though you can use it to edit or create spreadsheets.
#Who invented the computer?
Many people throughout history are credited with developing early prototypes that led to the modern computer. During World War II, physicist John Mauchly, engineer . Presper Eckert, Jr., and their colleagues at the University of Pennsylvania designed the first programmable general-purpose electronic digital computer, the Electronic -Numerical Integrator and Computer (ENIAC).
English mathematician and inventor Charles Babbage is credited with having conceived the first automatic digital computer. During the mid-1830s Babbage developed plans for the Analytical Engine.
Charles Babbage

#What can computers do?
Let us tell you about what a computer does. A computer is a machine that is very fast and versatile that can perform simple arithmetic operations, such as addition, subtraction, multiplication and division, and can also solve complex mathematical formulas. The most powerful computers can perform extremely complex tasks, such as simulating nuclear weapon experiments and predicting the development of climate change. The development of quantum computers, machines that can handle a large number of calculations through quantum parallelism (derived from superposition), would be able to do even more-complex tasks.
#classification of computer
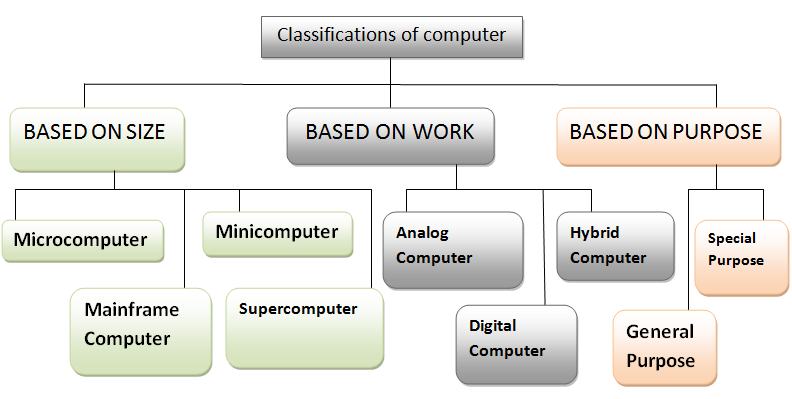
Based on size
Microcomputers became the most common type of computer in the late 20th century. The term “microcomputer” was introduced with the advent of systems based on single-chip microprocessors. The best-known early system was the Altair 8800, introduced in 1975. The term “microcomputer” has practically become an anachronism.
Minicomputers (colloquially, minis) are a class of multi-user computers that lie in the middle range of the computing spectrum, in between the smallest mainframe computers and the largest single-user systems (microcomputers or personal computers).
A mainframe computer, informally called a mainframe or big iron,is a computer used primarily by large organizations for critical applications like bulk data processing for tasks such as censuses, industry and consumer statistics, enterprise resource planning, and large-scale transaction processing.
A supercomputer is a computer with a higher level of performance than a general purpose computer. Supercomputer performance is commonly measured by Floating-point operations per second (FLOPS) instead of million instructions per second (MIPS). more information about classes os computer then you can visit our blog link here….
Based on work
An analog computer or analogue computer is a type of computer that uses the continuously variable aspects of physical phenomena such as electrical, mechanical, or hydraulic quantities to model the problem being solved. In contrast, digital computers represent varying quantities symbolically and by discrete values of both time and amplitude.
Digital computer, any of a class of devices capable of solving problems by processing information in discrete form. It operates on data, including magnitudes, letters, and symbols, that are expressed in binary code—i.e., using only the two digits 0 and 1. By counting, comparing, and manipulating these digits or their combinations according to a set of instructions held in its memory, a digital computer can perform such tasks as to control industrial processes and regulate the operations of machines; analyze and organize vast amounts of business data.
Hybrid computers are computers that exhibit features of analog computers and digital computers. The digital component normally serves as the controller and provides logical and numerical operations, while the analog component often serves as a solver of differential equations and other mathematically complex equations.
Based on purpose
Special purpose computers have little same features as a general-purpose computer has. But due to the absence of versatility, this computer completely differs from general ones. The special-purpose computer system is used for high graphic video games, a navigational system of an aircraft, oil exploration, weather forecasting, satellite launch/tracking, and automotive industries, traffic lights control system, washing machines, etc.
A general-purpose computer is one that, given the appropriate application and required time, should be able to perform most common computing tasks.Personal computers, including desktops, notebooks, smartphones and tablets, are all examples of general-purpose computers. The term is used to differentiate general-purpose computers from other types, in particular the specialized embedded computers used in intelligent systems.
