“DNS” stands of domain name system. it is responsible for translating domain names into a specific IP address so that the initiating client can load the requested Internet resources. Domain Name System (DNS) is a hierarchical naming system built on a distributed database for computers, services, or any resource connected to the Internet or a private network. this article we will discuss about what is dns in computer network.
Meaning of DNS server:
The DNS directory is distributed worldwide, stored in special servers called dns servers that are interconnected and communicate regularly to synchronize directory information and create redundancy. DNS servers translate requests for specific domains into IP addresses, controlling which server users with access when they enter the domain name into their browser.
For example, if someone types “example.com” into a web browser, a server behind the scenes maps that name to the corresponding IP address. An IP address is similar in structure to 203.0.113.72. for more deatils about dns click here…
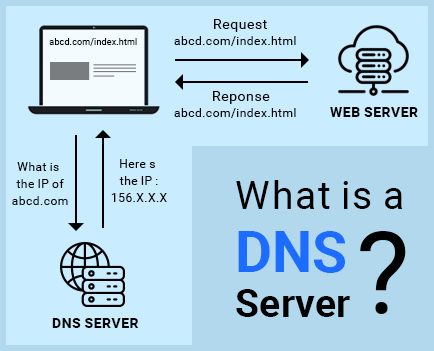
You may have come across the term “DNS server” before but weren’t sure what it referred to. This article aims to answer the question what is a DNS server as well as explain how they work. All domain names are associated with a particular IP address. and here we can real time example of IP address. This can be compared to a phonebook where a person’s name would correspond to the domain name (e.g. yourwebsite.com) and their phone number would correspond to the website’s IP (e.g. 159.x.x.x).
These IP address lookups are performed by DNS servers. The actual process of how a DNS server works is explained in greater detail in the section below.
How DNS Servers Work?
Here we can explain how dns servers work. The domain name system works much like a phone book where users can search for a requested person and retrieve their phone number.

The DNS directory that matches name to numbers isn’t located all in one place in some dark corner of the internet. With more than 332 million domain names listed at the end of 2017, a single directory would be very large indeed. Like the internet itself, the directory is distributed around the world, stored on domain name servers (generally referred to as DNS servers for short) that all communicate with each other on a very regular basis to provide updates and redundancies.
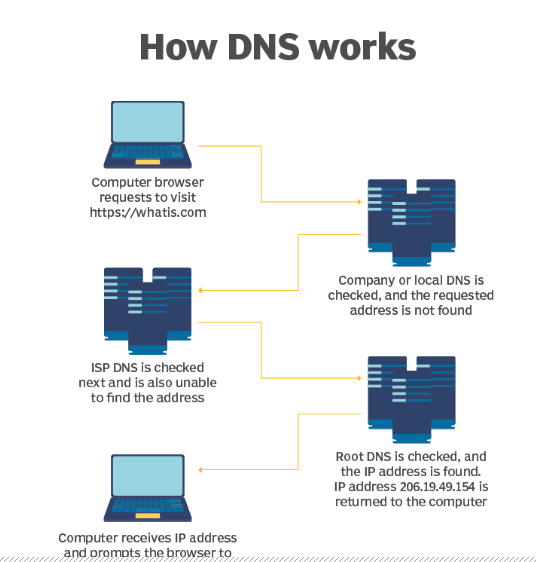
Basic process of a DNS resolution follows these steps:
- The user enters a web address or domain name into a browser.
- The browser sends a message, called a recursive DNS query, to the network to find out which IP or network address the domain corresponds to.
- The query goes to a recursive DNS server, which is also called a recursive resolver, and is usually managed by the internet service provider (ISP). If the recursive resolver has the address, it will return the address to the user, and the webpage will load.
- If the recursive DNS server does not have an answer, it will query a series of other servers in the following order: DNS root name servers, top-level domain (TLD) name servers and authoritative name servers.
- The three server types work together and continue redirecting until they retrieve a DNS record that contains the queried IP address. It sends this information to the recursive DNS server, and the webpage the user is looking for loads. DNS root name servers and TLD servers primarily redirect queries and rarely provide the resolution themselves.
- The recursive server stores, or caches, the A record for the domain name, which contains the IP address. The next time it receives a request for that domain name, it can respond directly to the user instead of querying other servers.
How do you find your DNS server?
If you want to see which servers are your primary then here are we can explain about how do you find dns server using command prompt.
The easiest way to determine what DNS server you’re using is via Windows Command Prompt.
- In Windows 10, right-click on the Start menu and click on Command Prompt (or Windows PowerShell either will do). In most other versions of Windows, click on Start, then All Programs, then Accessories, and finally on Command prompt.
- Type “ipconfig /all” followed by Enter. You’ll get a lot of information.
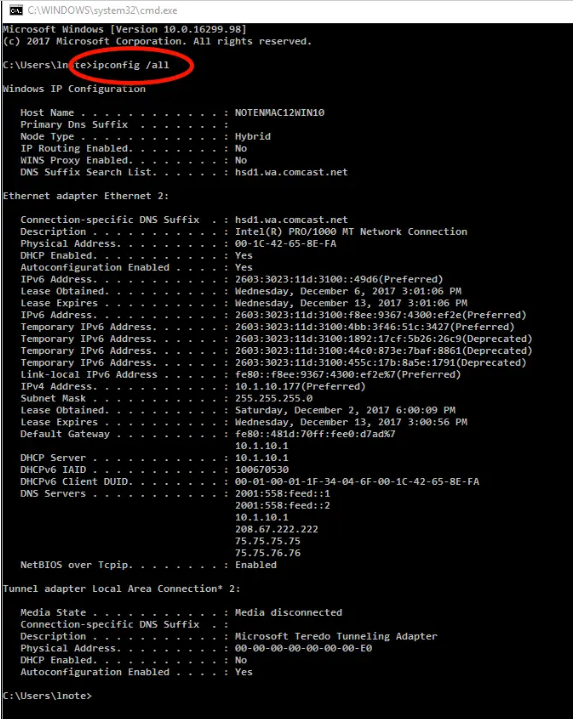
- In the midst of all that information, you can see “DNS Servers” listed. Typically, there are multiple servers that provide backup access if one fails to respond.

In this article we have try to define “what is dns in computer network?”. Hope you are like it! Thanks for reading this article.
