In computing, a server is a piece of computer hardware or software (computer program) that provides functionality for another program or device, called a “client“. This The architecture is called the client-server model. Servers can provide various functionalities, often referred to as “services“, such as sharing data or resources among multiple Performing calculations for the client, or the client. A single server can serve multiple clients, and a single client can use multiple servers.
The client process can start Can connect to a server on the same device or a different device on a network. Typical servers are database servers, file servers, mail servers, print servers, Web Servers, Game Servers and Application Servers Client–server systems are usually implemented by (and often identified with) the request–response model: the client sends a request to the server, which performs some action and sends a response to the client, usually with a result or acknowledgment. With. Designating a computer as “server-class hardware” implies that it is specific to the server to run on. This often means that it is more powerful and reliable than standard personal computers, but alternatively, large computing clusters can be composed of many relatively simple, replaceable server components.

Types of server
Database server:
A database server is a server that uses a database application to provide database services to other computer programs or computers, as defined by the client and in some database management systems (such as MySQL) client-side for database access. Servers rely exclusively on the model (while others, such as SQLite, are intended for use as an embedded database). Users access the database server either through a “front end” running on the user’s computer – which displays the requested data – or through a “back end”, which runs on the server and performs tasks such as data analysis and storage. handles. In a master-slave model, the database master servers are the central and primary location of data while the database slave servers are synchronized backups of the master acting as a proxy. Most database applications respond to a query language. Each database understands its own query language and converts each submitted query into a server-readable form and executes it to retrieve the results.

Examples of proprietary database applications include Oracle, DB2, Informix, and Microsoft SQL Server. Examples of free software database applications include PostgreSQL; and Ingres and MySQL are included under the GNU General Public License. Each server uses its own query logic and structure. The SQL query language is more or less the same on all relational database applications. To clarify, a database server is simply a server that maintains services related to clients through database applications.
File server:
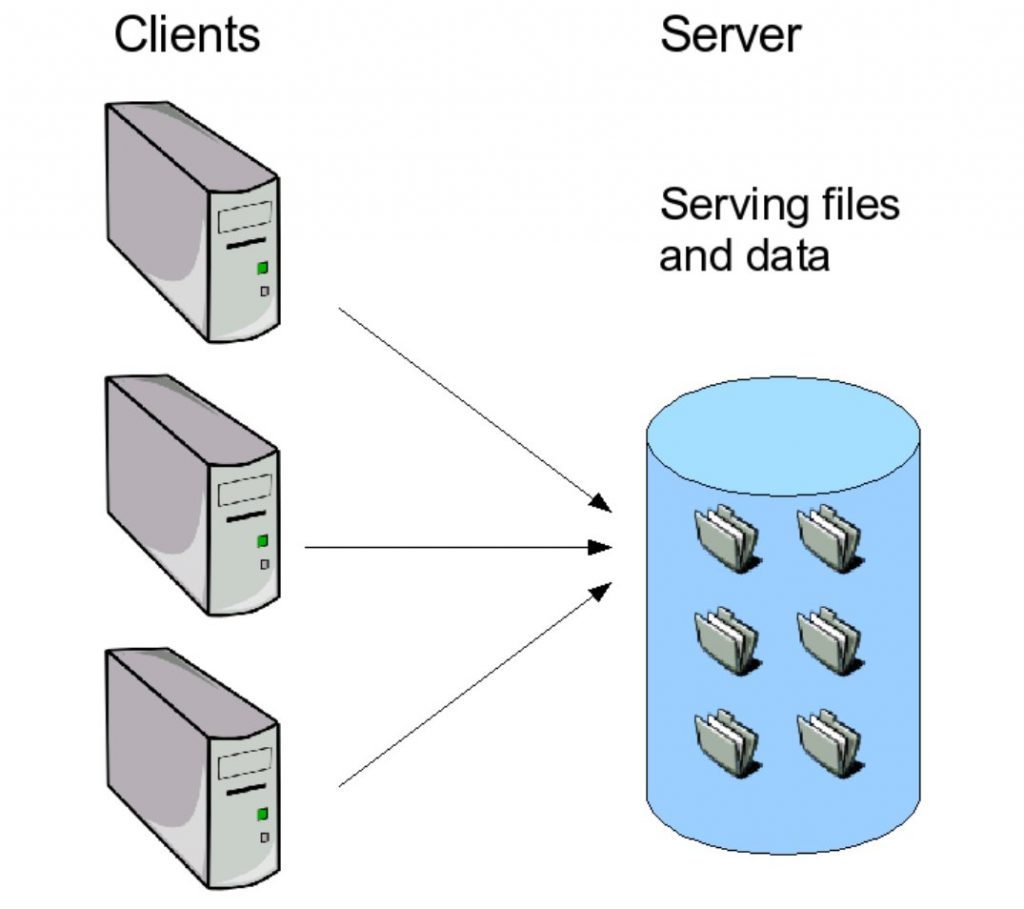
In computing, a file server (or fileserver) is a computer connected to a network that provides a location for shared disk access, i.e. the storage of computer files (such as text, images, sound, video) that can be accessed by those workstations. can be accessed by computers that are able to access computers that share access through a computer network. Server highlights the role of the machine in the traditional client-server scheme, where the clients are the workstations that use the storage. A file server does not typically run computational tasks or programs on behalf of its client workstations. File servers are commonly found in schools and offices, where users use local area networks to connect their client computers.
Web server:
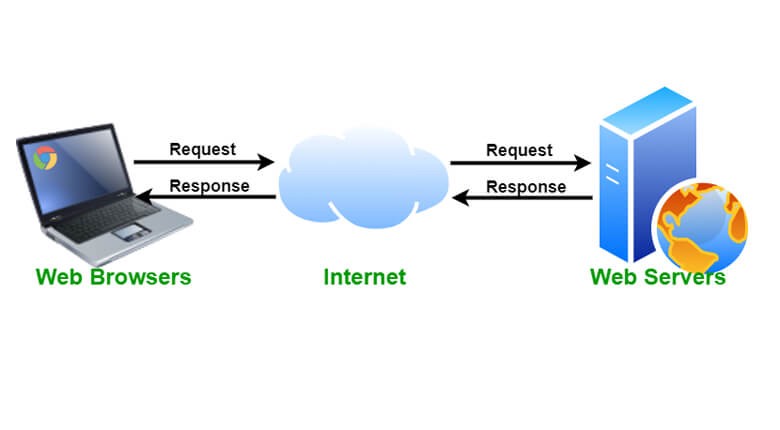
A web server is computer software and underlying hardware that accepts requests via HTTP, the network protocol created for delivering web content, or its secure version HTTPS. A user agent, typically a web browser or web crawler, initiates communication by making a request for a specific resource using HTTP, and the web server responds with that resource’s content or error message. The web server can also accept and store resources sent from the user agent A web server can be a single computer, i.e. a desktop, a laptop or even an embedded system (such as a router, a printer, a webcam, etc.) with a built-in configuration. interface, but high-traffic websites typically run web servers on a fleet of server computers designed to handle the large number of requests for documents, multimedia files and interactive scripts.
Terminal server:
A terminal server connects devices with a serial port to a local area network (LAN). Products marketed as terminal servers can be very simple devices that do not offer any security functionality, such as data encryption and user authentication. The primary application scenario is to enable serial devices to access network server applications, or vice versa, where security of the data on the LAN is not generally an issue. There are also many terminal servers on the market that have highly advanced security functionality to ensure that only qualified personnel can access various servers and that any data that is transmitted across the LAN, or over the Internet, is encrypted.
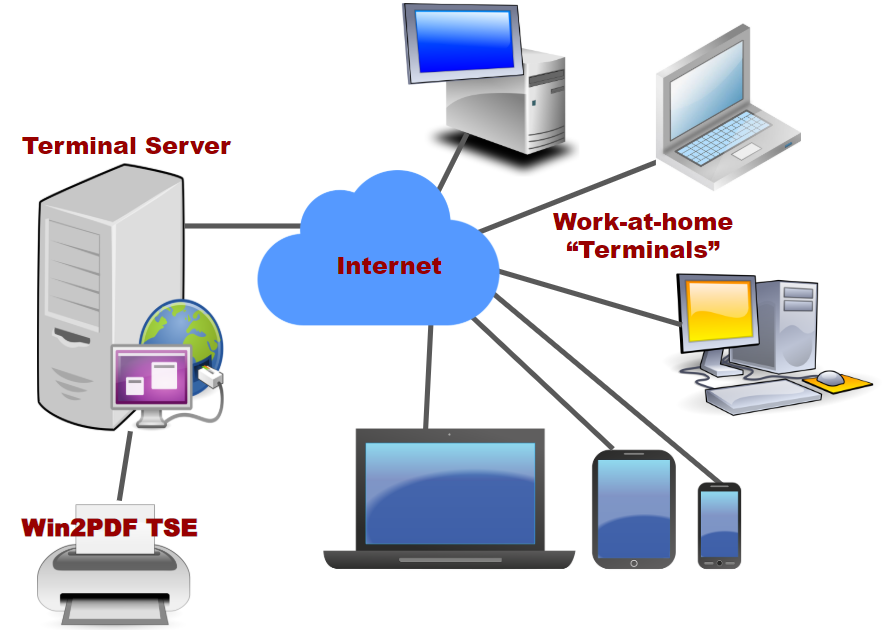
Usually, companies that need a terminal server with these advanced functions want to remotely control, monitor, diagnose and troubleshoot equipment over a telecommunications network.A console server (also referred to as console access server, console management server, serial concentrator, or serial console server) is a device or service that provides access to the system console of a computing device via networking technologies.
