This article we will explain about which ip address is class c then answer is that Address 192.168. 123.132 is a Class C address. Class C networks use a default subnet mask of 255.255.255.255. 255.0 and have 192-223 as their first octet. Class C addresses are commonly used for small to mid-size businesses.
What is a class C IP Address(192.168. 123.132)?
To assure the superiority of a website, each search engine analyzes all of your backlinks and the page rank of your site. Large companies can exploit these to make certain that their company website will rank on at the top of Google and Bing search engine listings. One way a website can gain such an advantage is listings across the web is by having their own Class C IP Address.

Search Engine Optimization with Class C network address is a straightforward form of hosting services that uses different C Class IP hosting addresses. The C Class IP addresses always contain four unique blocks. An example is 123.456.789.1. In this example, the server is hosted on the “789” C block and has a unique value that can help provide equity to links that you may have between multiple sites. A mixture of algorithms are used for Google to take this block of code and provide the location of the hosting of the website.
To assure the superiority of a website, each search engine analyzes all of your backlinks and the page rank of your site. Large companies can exploit these to make certain that their company website will rank on at the top of Google and Bing search engine listings. One way a website can gain such an advantage is listings across the web is by having their own Class C IP Address.
Types of Network classes:
IP addresses are divided into classes. The most common of them are classes A, B and C. Classes D and E exist, but are not used by end users. Each address class has a different default subnet mask. You can identify the class of an IP address by looking at the first octet of it. The following are categories of Class A, B and C Internet addresses, each of which has an example address:
Class A
Class A networks use a default subnet mask of 255.0.0.0 and have 0-127 as their first octet. The address 10.52.36.11 is a class A address. Its first octet is 10, which is between 1 and 126, inclusive.
Class B
Class B networks use a default subnet mask of 255.255.0.0 and have 128-191 as their first octet. The address 172.16.52.63 is a class B address. Its first octet is 172, which is between 128 and 191, inclusive.
Class C
Class C networks use a default subnet mask of 255.255.255.0 and have 192-223 as their first octet. The address 192.168.123.132 is a class C address. Its first octet is 192, which is between 192 and 223, inclusive.
Advantages of Class C IP Addresses:
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO), or SEO hosting with Class C IP Address is a simple variety of hosting service that utilizes different C Class IP Addresses.
- It’s well known that any type of IP address always contains four different blocks simply like a telephone number.
The many algorithms of Google are effective at using this code block thereby representing the location of the hosting of the website. - As is common knowledge, every internet-connected machine on a network has an address, much like your house.
- This address is referred to as an Internet Protocol (IP) address.
- IP addresses, due to binary restrictions, are confined to unique range.
- Displayed as decimals, an IP address can read anywhere from 0.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.255.
Other terms related to IP address:
IP is the network protocol used for sending network packets over a TCP/IP network or the Internet.and IP Address is a unique 32-bit address for a host on a TCP/IP network or internetwork. TCP/IP networks are divided into networks and subnetworks. A subnet mask is used to divide an IP address into two parts. One part identifies the host (computer), the other part identifies the network to which it belongs. To better understand how IP addresses and subnet masks work, let’s look at an IP address.
subnet mask:
The subnet mask is used by the TCP/IP protocol to determine whether a host is on a local subnet or on a remote network. Network information is provided in another 32-bit number called the subnet mask. By adding the IP address and the subnet mask together, the network and host portion of the address can be separated; the first 24 bits (the number of the subnet mask) are identified as the network address. The last 8 bits (the number of remaining zeros in the subnet mask) are identified as the host address. This gives you the following addresses:
11000000.10101000.01111011.00000000 – Network Address (192.168.123.0)
0000000000000000000000000000000100100 – Host Address (0000.000000.132)
For example using the 255.255.255.0 subnet mask, that network ID is 192.168.123.0, and the host address is 0.0.0.132. When a packet arrives on the 192.168.123.0 subnet (from the local subnet or remote network), and its destination address is 192.168.123.132, your computer will receive it from the network and process it.
IP addresses: Networks and hosts
An IP address is a 32-bit number. It uniquely identifies a host (computer or other device, such as a printer or router) on a TCP/IP network. IP addresses are usually expressed in dotted-decimal format, with four numbers separated by periods, such as 192.168.123.132.
For example, the dotted-decimal IP address 192.168.123.132 (in binary notation) is a 32-bit number 110000000101000111101110000100. This number can be difficult to understand, so it is divided into four parts of eight binary digits; these 8-bit sections are known as octets. The IP address then becomes 11000000.10101000.01111011.10000100.
For a TCP/IP wide area network (WAN) to work efficiently as a collection of networks, routers that pass packets of data between networks do not have to know the exact location of the host. Know which network the host is a member of After the packet is delivered to the destination’s network, the packet is forwarded to the appropriate host. For this process to work, an IP address has two parts. The first part of the IP address is used as the network address, the last part as the host address. If you take the example of 192.168.123.132 and divide it into these two parts, you get 192.168.123. network .132 host or 192.168.123.0 – network address. 0.0.0.132 – host address.
What is Class C and its addresses:
Class C IP addresses range from 192-223 in the first byte and are designed to be used in small-sized companies. IP addresses with a first octet from 192 to 223 are part of this class. Class C addresses also include the second and third octets as part of the Net identifier. The last octet is used to identify each host. This means that there are 2,097,152 (221) Class C networks each with 254 (28 -2) possible hosts for a total of 536,870,912 (229) unique IP addresses.
Class C addresses:
A Class C address consists of a 24-bit network address and an 8-bit local host address.
The first three bits in the network address indicate the network class, leaving 21 bits for the actual network address. Therefore, there are 2,097,152 possible network addresses and 256 possible local host addresses. In a Class C address, the highest order bits are set to 1-1-0.
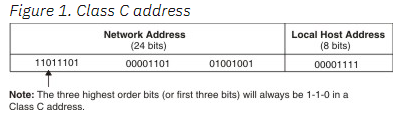
The first 24 bits contain the network address (the three highest order bits will always be 1-1-0). The remaining 8 bits contain the local host address. When deciding which network address class to use, you must consider how many local hosts there will be on the network and how many subnetworks will be in the organization. If the organization is small and the network will have fewer than 256 hosts, a Class C address is probably sufficient. If the organization is large, then a Class B or Class A address might be more appropriate. In other words, the first octet of a Class C address is in the range 192 to 223.
