ISPs All network access points are interconnected through public network facilities on the Internet backbone. The rise of commercial Internet services and applications helped fuel the rapid commercialization of the Internet. There was the rise of Ethernet and other “local area networks” (LANs) for connecting personal computers. But other forces were also at work. Following the reorganization of AT&T Corporation in 1984, the US National Science Foundation took advantage of various new options for its national-level digital backbone service, known as NSFNET. In 1988 the US Corporation for National Research Initiatives was approved for an experiment to connect a commercial e-mail service (MCI Mail) to the Internet. The application was the first internet connection for a commercial provider that was not even part of the research community. Approval soon followed to allow access to other e-mail providers.

What is ISP in computer with example?
The term Internet Service Provider (ISP) refers to a company, that provides Internet connections and services to individuals and organizations. ISPs make it possible for their customers to surf the web, shop online, conduct business, and connect with family and friends—all for a fee. ISPs may also provide other services including email services, domain registration, web hosting, and browser packages. An ISP may also be referred to as an information service provider, a storage service provider, an Internet service provider (INSP), or any combination of these three based on the services the company offers. In addition to providing access to the Internet, ISPs may also provide software packages (such as browsers), e-mail accounts, and a personal Web site or home page. ISPs can host web sites for businesses and can also build web sites themselves.

Example:
An Internet Service Provider (ISP) is a company such as AT&T, Verizon, Comcast, or Spectrum that provides Internet access to companies, families, and even mobile users. ISPs use fiber-optics, satellite, copper wire, and other forms to provide Internet access to its customers.
Main points of Internet Service Provider (ISP):
Internet service provider (ISP) is a company that provides web access to both businesses and consumers.
ISPs may also provide other services such as email services, domain registration, web hosting, and browser services.
An ISP is considered to be an information service provider, storage service provider, Internet network service provider (INSP), or a mix of all of them.
Internet use has evolved from only those with university or government accounts having access to nearly everyone having access, whether it’s paid or free.
Access has gone from dial-up connections to high-speed broadband technology.
How do ISPs work?
If you read this, you will know that what ISPs do is they are connected to one or more high-speed Internet lines. Larger ISPs have their own high-speed leased lines, so they are less dependent on telecommunications services and can provide better service to their customers. Many ISPs are also connected to large backbone routing centers. ISPs also place thousands of servers in data centers. The number of servers depends on their Internet service area. These large data centers manage all the customer traffic.
ISPs are divided into the following three levels:
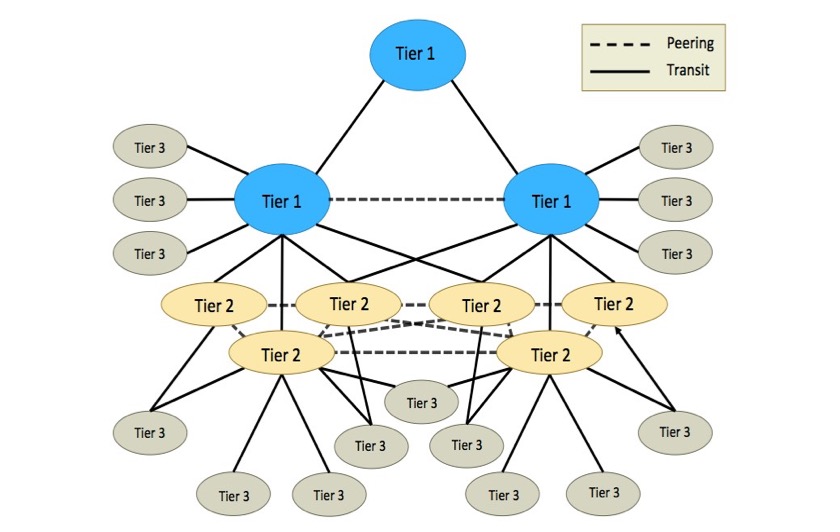
Tier 1 ISP:
Tier 1 ISPs have the most global reach and enough physical network lines to carry most of the traffic on their own. They also interact with other Tier 1 networks to allow free traffic through other Tier 1 providers. Tier 1 ISPs usually sell network access to Tier 2 ISPs.
Tier 2 ISP:
Tier 2 ISP networks are focused on consumer and commercial customers. And ISPs have regional or national reach and are the service providers that connect Tier 1 and Tier 3 ISPs. They have to buy access to the larger Tier 1 networks, but are equivalent with other Tier 2 ISPs.
Tier 3 ISP:
Tier 3 ISPs focus on providing Internet access to local businesses and consumer markets. And ISPs connect customers to the Internet using another ISP’s network. Tier 3 ISPs use and pay higher tier ISPs for access to Internet services.
In this article you can read about “What does ISP stand for in computer terms?” and it’s work. hope this article is helpful to you.
