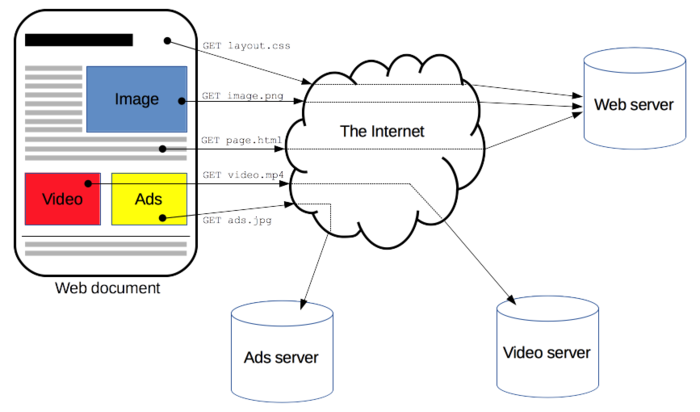
HTTPS stands for Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure and is one of the ways that websites can provide Internet users with an extra layer of security and privacy while browsing the Internet and accessing various online resources. To understand HTTPS, you must first understand HTTP, which stands for Hypertext Transfer Protocol. This protocol is what allows your browser to communicate with the websites you visit online as well as with the web servers that host them.
What does “HTTPS” mean in a web address?
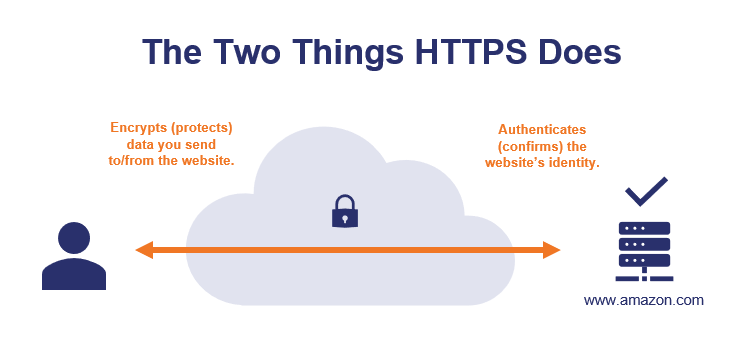
If you see HTTPS, the session between the web server and the browser on the mobile device you are using is encrypted. You can easily identify web servers that have HTTPS configured by looking at the Uniform Resource Locator (URL) in your browser’s web address bar.
Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure is a combination of Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) with Secure Sockets Layer (SSL)/Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocols. TLS is an authentication and security protocol widely implemented in browsers and web servers. SSL works by using the public key to encrypt the data transferred over an SSL connection. Most web browsers support SSL. It allows you to securely communicate with the web server.
Why should you use HTTPS?
There are several good reasons to use HTTPS on your website and to insist on HTTPS when browsing, shopping, and working on the web as a user :
Integrity and Authentication: Through encryption and authentication, HTTPS protects the integrity of communication between a website and a user’s browser. Your users will know that data sent from your web server has not been intercepted and/or altered by any third party in transit. And, if you have made additional investments in EV or OV certificates, they will also be able to tell whether the information actually came from your business or organization.
Privacy: Certainly no one wants intruders to spy on your credit card numbers and passwords while shopping or banking online, and HTTPS is great for preventing that. But do you really want everything you see and do on the web to be an open book for anyone who wants to spy on you to build a profile (which includes governments, employers, or anyone else?) Who wants to anonymize online activities?)? HTTPS plays an important role here as well.
User Experience: HTTP sites have been flagged as unsafe as a result of recent changes to the browser UI. Do you want your customers’ browsers to tell them your website is “not secure” or show them a crossed-out lock when they visit it? no, at all!
Compatibility: Current browser changes are moving HTTP closer to incompatibility. Mozilla Firefox recently announced an optional HTTPS-only mode, while Google Chrome is pushing to block mixed content (HTTP resources associated with HTTPS pages). When viewed with browser warnings of “vulnerabilities” for HTTP websites, it’s easy to see that the writing is on the wall for HTTP. In 2020, all current major browsers and mobile devices support HTTPS, so you won’t lose users by switching from HTTP.
SEO: Search engines (including Google) use HTTPS as a ranking signal when generating search results. Therefore, website owners can get an easy SEO boost by simply configuring their web servers to use HTTPS instead of HTTP.
How does Hypertext transfer protocol secure work?
Hypertext transfer protocol secure uses an encryption protocol to encrypt communication. The protocol is called Transport Layer Security (TLS), although it was previously known as Secure Sockets Layer (SSL). This protocol secures communications by using what is known as an asymmetric public key infrastructure. This type of security system uses two different keys to encrypt the communication between two parties:
- Private Key – This key is controlled by a website owner and is kept, as the reader might have guessed, private. This key resides on a web server and is used to decrypt information encrypted by the public key.
- Public Key – This key is available to anyone who wants to interact with the server in a secure manner. Information encrypted by the public key can only be decrypted by the private key.
The benefit of the Hypertext transfer protocol is secure –
- Secure communication: HTTPS creates a secure connection by establishing an encrypted link between the browser and the server or any two systems.
- Data integrity: HTTPS provides data integrity by encrypting the data and hence, even if hackers manage to trap the data, they cannot read or modify it.
- Privacy and Security: HTTPS protects the privacy and security of website users by preventing hackers from passively listening to the communication between the browser and the server.
- Faster performance: Increases data transfer speed by encrypting and reducing the size of HTTPS data as compared to HTTP.
- SEO: Using HTTPS increases the ranking of SEO. In Google Chrome, if users’ data is collected over HTTP, Google shows the Not Secure label in the browser.