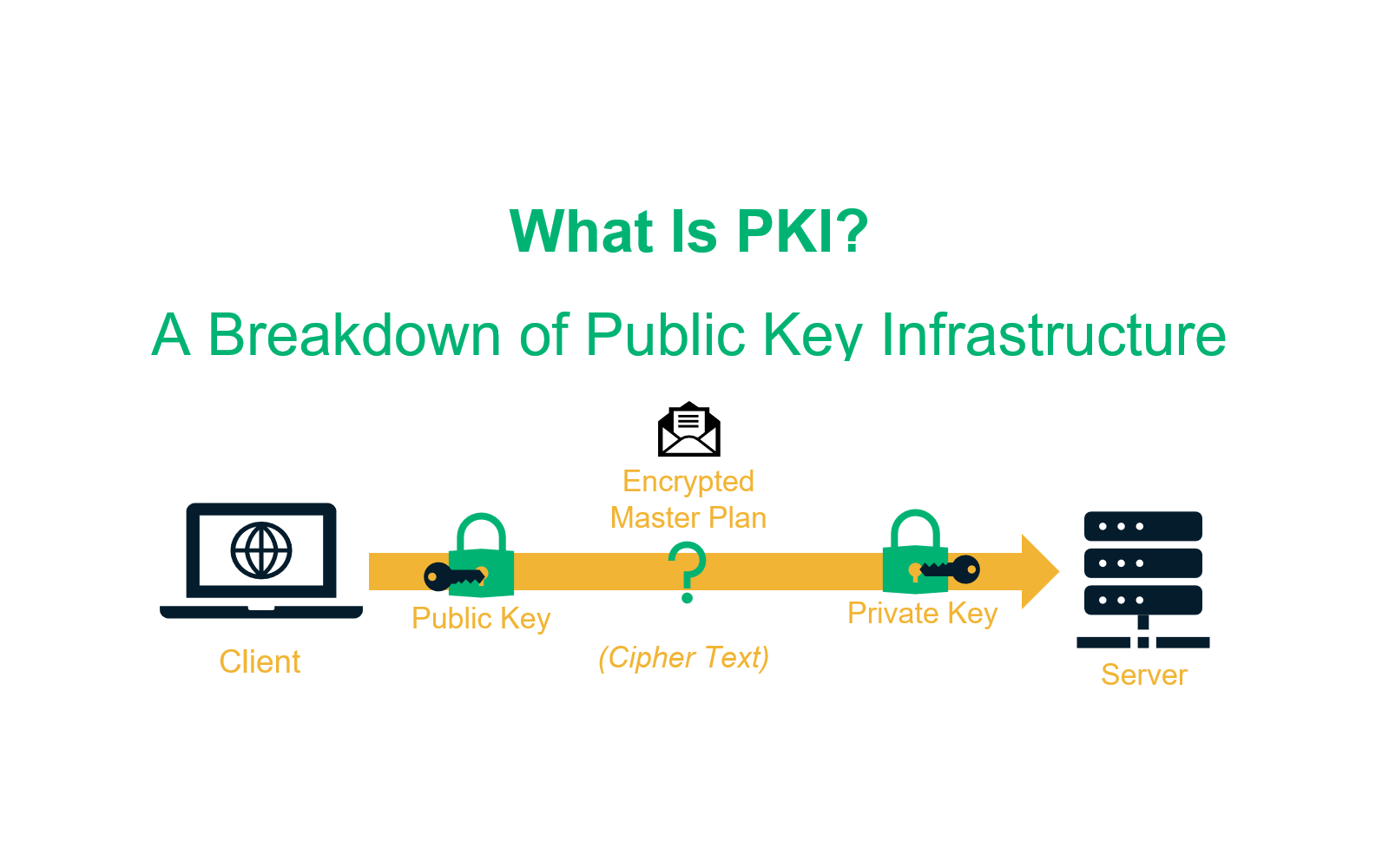
In this article we will discuss what is pki. and will explain about the role of digital certificates as well as what can pki be used for and how pki works. so you can read this below.
Definition of pki:
In this we will explain what is pki PKI performs direct encryption through the keys it generates. It works by using two different cryptographic keys: a public key and a private key. Keys are public or private, they encrypt and decrypt secure data. A public key infrastructure (PKI) is a set of roles, policies, hardware, software, and processes required to create, manage, distribute, use, store and revoke digital certificates and manage public-key encryption. The purpose of PKI is to facilitate the secure electronic transfer of information for many network activities such as e-commerce, Internet banking and confidential email.
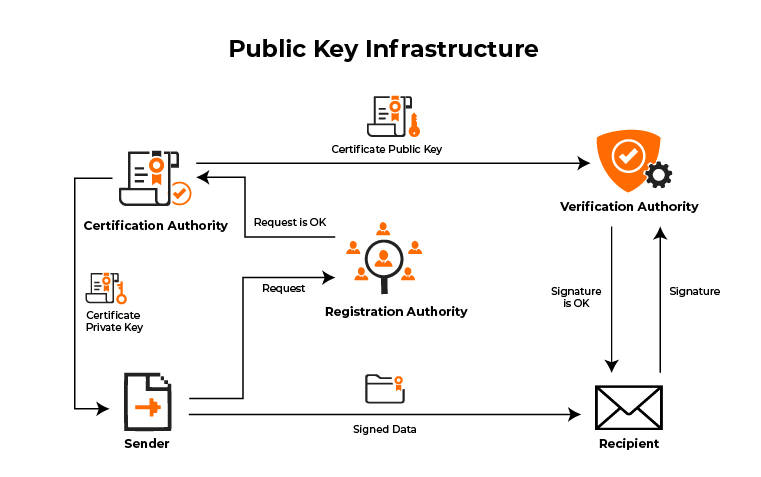
RA is responsible for accepting requests for digital certificates and authenticating the requesting entity. below section we will describe about role of certificate authorities. The role of the PKI is called the Registration Authority (RA) by the CA to ensure valid and correct registration.
Role of Digital Certificates:
Digital certificates are also called X.509 certificates and PKI certificates. you refer to them, a digital certificate has these qualities:
- Is an electronic equivalent of a driver’s license or passport
- Contains information about an individual or entity
- Is issued from a trusted third party
- Is tamper-resistant
- Contains information that can prove its authenticity
- Can be traced back to the issuer
- Has an expiration date
- Is presented to someone (or something) for validation
What can a PKI be used for?
The most common applications of a PKI include Wi-Fi authentication, web application authentication, email security, and VPN. Below we’ll demonstrate how each is tied to the PKI.
WI-FI authentication:
Users with a certificate signed by the trusted CA can connect to the secure SSID and be authenticated by the RADIUS server using EAP-TLS. and it authentication encrypts data sent through it and protects from over-the-air attacks using wi-fi. The certificate is sent and the RADIUS confirms their identity, establishing trust that grants secure network access.
Web application authentication:
It is similar to Wi-Fi authentication, a user connecting to a web application will have their identity confirmed by the web application server. Since the certificate is signed by the trusted CA, they are able to gain access to the application.
Email security:
Encrypting emails(if you create an email then click the link) with certificates utilizes the S/MIME (Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions) protocol. Both the receiver and sender are required to have a certificate signed by the CA to establish trust between the users. S/MIME provides the cryptographic security required to guarantee the origin of the message with the digital signature from the certificate, encrypt the message, and authenticate the recipient’s certificate to decrypt the message.
How does PKI work?
The most important concepts to understand how PKI works are keys and certificates. A key, as already mentioned, is a long string of bits a number, in other words that is used to encrypt the data. Obviously the math behind modern encryption is much more complicated than this.
PKI gets its name because each participant in a secure communication channel has two keys. There is a public key, which you can reveal to anyone who asks and is used to encode the message sent to you, and a private key, which you keep secret and used to decrypt the message when it is received. use for. The two keys are related by a complex mathematical formula that would be difficult to derive with brute force.
One of the ways it gets around a somewhat obvious problem with Caesar ciphers: You have to somehow tell your recipient the key used to encode the encrypted message.
So that the data can be encrypted within the public key infrastructure. PKI is widely used because, in addition to encrypting messages, it tells you the person with whom you are exchanging encrypted messages. This is where certificates come in.