SCCM stands for System Center Configuration Manager, and it is an offering from the Microsoft suite of products that helps organizations manage their infrastructure on a day-to-day basis.
Microsoft System Center Configuration Manager (SCCM) is a Windows product that enables the management, deployment and security of devices and applications across an enterprise. It keeps track of a network’s inventory, assists in application installation, and deploys updates and security patches across a network.
Microsoft SCCM purpose is to built or manage Windows clients but with the help of the Parallels Mac Management plug-in, it can also handle Mac clients conveniently – and straight from the SCCM console as well.
SCCM (System Center Configuration Manager) OVERVIEW:
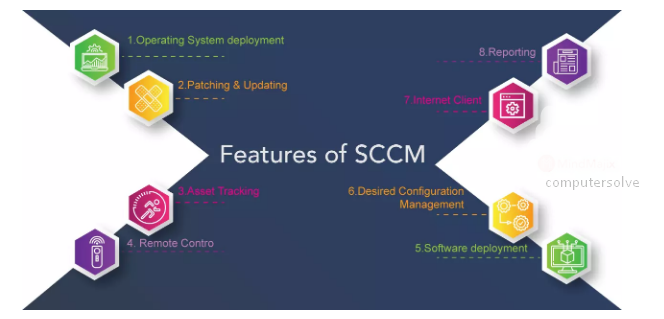
Features of System Center Configuration Manager (SCCM):
- Provides improved workflow to create mobile device configuration items.
- Deduplication feature and compression very easy to use.
- Provides support to the Always On feature on SQL Server to provide highly available databases.
- Windows management : To keep pace with updates to Windows 10.
- Endpoint protection : To provide identification and malware protection.
- Reporting : To present information on users, hardware & software, applications and software updates.
- Operating system (OS) deployment : To distribute operating systems to devices in an enterprise.
- Software update management : Allows users administrators to deliver and manage updates to devices across an enterprise.
- Application delivery: Allows administrators to deliver an application to all devices across an enterprise.
- Deployment of operating systems.
- Patch management.
- Asset tracking.
- Remote control.
- Software deployment.
- Desired Configuration Management.
How SCCM (System Center Configuration Manager) Works?
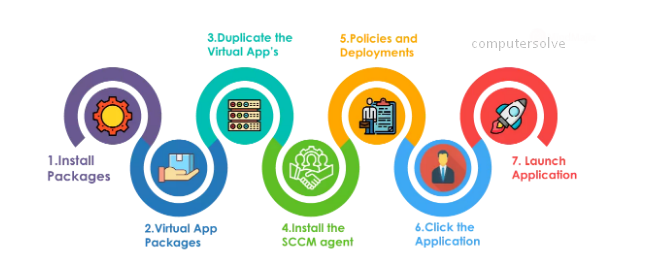
Step1: To install the application, first create packages in the SCCM console which consists of the command line and executed files.
Step2: Configuration manager admin creates virtual application packages and replicates to selected Distribution Points.
Step3: If the user wants to download any application, then the user can directly download the application from the distribution points rather than connecting to the SCCM primary server.
Step4: Now, install the SCCM agent which helps a machine to communicate with the SCCM servers.
Step5: In this step, the SCCM agent keeps on checking for the new policies and deployments. Using the updates SCCM admin creates deployment where an application is targeted on a bunch of machines.
Step6: Policy reaches the end machine, the SCCM agent evaluates the policy and reaches out to its particular regional distribution points for downloading the packages.
Step7: It will be executed files are downloaded in a temp folder, users can install those packages in the local system. Now the file status is sent back to the SCCM server to update in the database.
How to install SCCM (System Center Configuration Manager)?
Step 1: Execute Setup.exe from the SQL installation media.
Step 2: Select New SQL server stand-alone installation.
Step 3: Provide the product key and click Next.
Step 4: Review and Click Next.
If you want to know more steps about installing System Center Configuration Manager you have to read full article and learn various methods to install System Center Configuration Manager (SCCM) How to install SCCM?
What is the use of SCCM?
- One Client: The ConfigMgr client controlling all installations on a computer, both software updates and application installations. When using a standalone WSUS the ConfigMgr client and WSUS client often tries to install software updates at the same time, which results in an error that is a hazard both for the end-user and to the IT department.
- Reporting: There are many built-in reports for Software Update Compliance, troubleshooting and details. The reports combined with all the other information ConfigMgr holds about your clients in your environment you can easily create really powerful and customized reports that you need in your environment.
- Maintenance Windows: Maintenance Windows can be used to control when changes are allowed to be made to a specific system. This means that you deploy the update once and then based on Maintenance Windows the updates are installed and the servers are rebooted according to the deployment.
- Automatic deployment rules: This isn’t really a benefit compared to WSUS, but as it is a new feature of Configuration Manager 2012 I will still add it to the list. It is possible to automatically approve updates, download them and distribute them to the DP’s automatically, just as you would in WSUS.
- One Infrastructure: The actual software update files are downloaded from the local DP and not the WSUS/SUP server. It means that you will not need a separate WSUS infrastructure and the updates are downloaded from the DP which minimizes the WAN impact for remote sites.
- OS deployment integration: A built-in task is available and can be used to deploy software updates from Configuration Manager during the OS deployment in the Task Sequence.
- End-user experience: The software center is used for all end-user interaction, dialogs shown to the user all have the same look, making it easier for the end-user to understand what is happening.
- Targeting: Using query-based collections we get really powerful options for targeting. We can dynamically create a collection based on any value that exists in the database, for instance, divide all clients based on the last number in the computer name, and deploy software updates to computers with odd computers on one day and all with even numbers the day after.
- Offline Servicing of Images: If you use ConfigMgr 2012 for managing your Software Updates you can use the built-in feature to do offline servicing on your OS Images.
What is SCCM called today?
A big announce this year at Microsoft Ignite was that starting in version 1910, Configuration Manager is now part of Microsoft Endpoint Manager.
How much does SCCM cost?
SCCM can cost anywhere from $1M over three years for a typical 5,000 endpoint deployment and up to $14M a year for 200,000 endpoints according to IBM. This greatly outweighs the initial cost of an SCCM license, which costs $1,323 or is even included in Microsoft Software Assurance licensing.
